Case Study · Evaluating Modular Prompting with BrinPage CPM
Cost, Accuracy, and Context Efficiency in a Real Production Workflow
(Anonymized technical analysis · November 2025)
1. Overview
This case study analyzes the impact of using BrinPage CPM (Context Prompt Manager) in a real production environment inside a mid-sized professional firm. The company operates an internal AI assistant integrated into their intranet. Their workflow relies heavily on structured domain-specific information that must be provided as context for every model request.
We compared two approaches:
- Baseline (Monolithic Prompt)
- All context is concatenated into one long system prompt.
- No modularization.
- Same prompt structure for every request, regardless of relevance.
- BrinPage CPM (Modular Context System)
- Context is split into reusable modules.
- Only relevant modules are activated per request.
- Real-time preview and control through the local CPM dashboard (localhost:3027).
The goal was to evaluate cost efficiency, token usage, and answer quality using real queries aggregated from more than ~700 production calls.
2. Context Structure of the Client
The client maintains a comprehensive internal knowledge base organized into:
- 38 context modules
- Each module averaging ~500 words
- Total potential context size: ~19,000 tokens
Examples of module types (genericized):
- Project guidelines
- Technical standards
- Internal workflows
- Communication rules
- Domain-specific procedures
- Reference styles
- Legal or compliance notes
This dataset is ideal for testing CPM because it contains:
- High-overlap but highly heterogeneous information
- Modules that are not always relevant at the same time
- Ambiguities that often cause models to answer incorrectly when too much context is provided
3. Methodology
We conducted two parallel evaluations:
3.1 Token & Cost Evaluation
We compared the theoretical and real token usage under:
- Monolithic Prompt Approach
- Always send all 38 modules, regardless of relevance.
- CPM Modular Activation
- Activate only the modules needed for each query (typically 3–5).
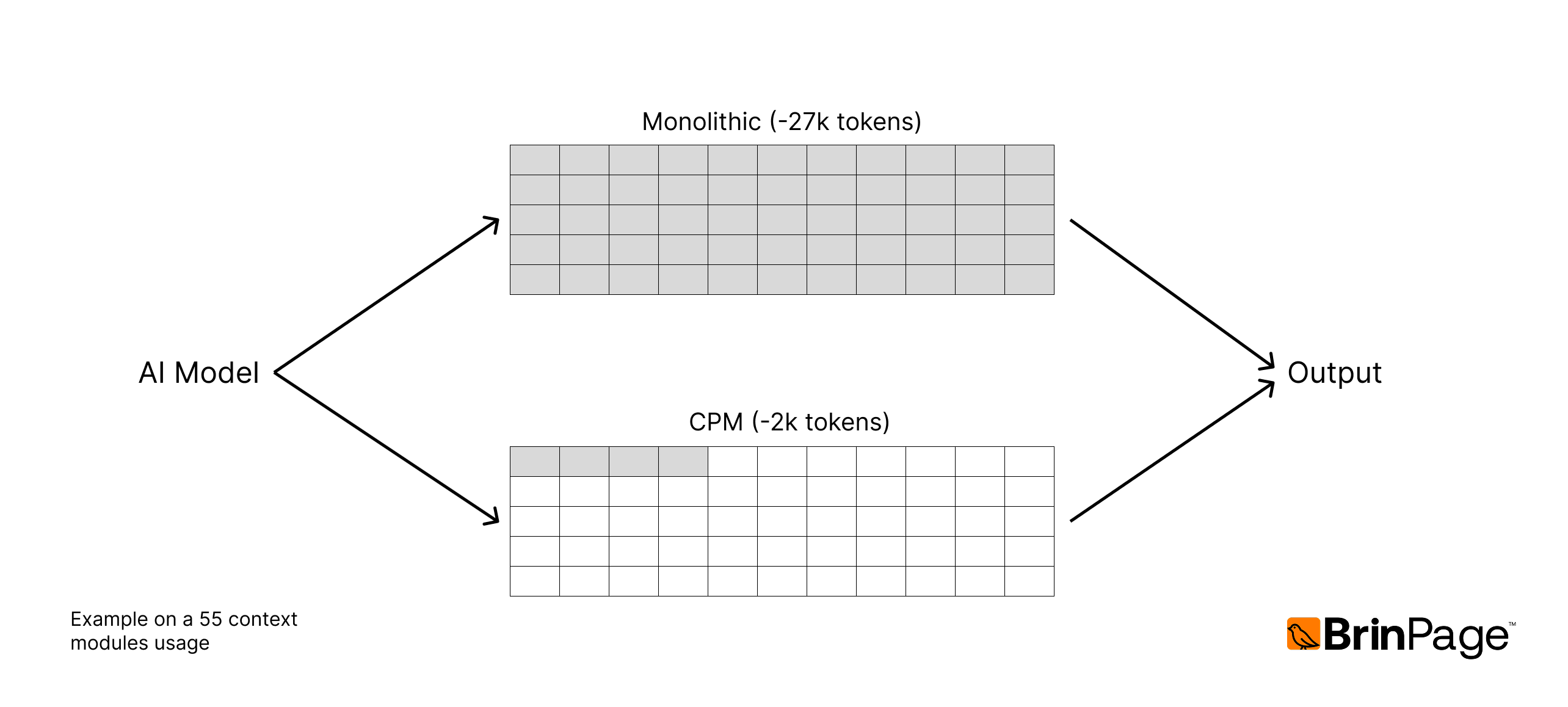
Token counts were measured using actual model requests sent through BrinPage Platform.
3.2 Accuracy Evaluation (Blind Human Review)
We selected 26 real queries from the client’s intranet logs. For each query:
- We generated two answers:
- A: Monolithic prompt (all modules, ~20k tokens)
- B: CPM modular prompt (3–5 modules, ~3k tokens)
- Reviewers inside the client’s team evaluated the responses blindly, without knowing which system generated which answer.
Reviewers rated each answer on:
- Relevance
- Technical accuracy
- Clarity and usefulness
- Consistency with internal standards
The better answer for each query was recorded.
4. Results
4.1 Token Usage Comparison
Token usage per approach:
| Approach | Avg. Input Tokens per Request | Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Monolithic Prompt | ~20,000 tokens | — |
| CPM Modular Prompt | ~3,000 tokens | ≈ 6–7× reduction |
This reduction was stable across all tested queries.
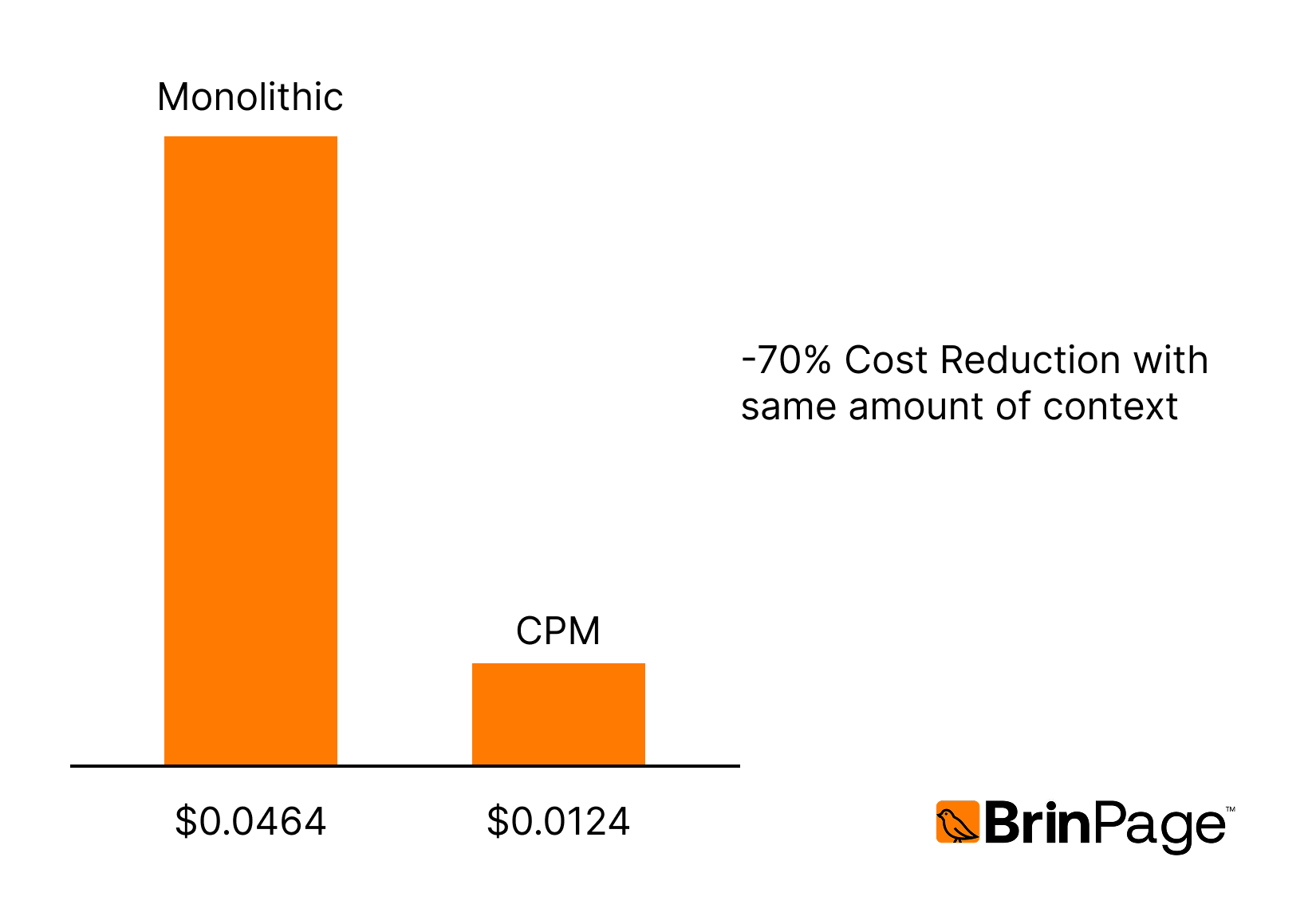
Cost Interpretation (GPT-4.1 pricing)
Input cost: $0.002 / 1k tokens. Output cost: similar for both methods.
Cost per request:
- Monolithic: ~$0.0464
- CPM: ~$0.0124
→ ≈ 70% cost reduction for the same operational workload.
This is consistent with real usage:
Over ~700 production calls, CPM saved tens of thousands of tokens per day.
4.2 Accuracy & Quality Comparison
In the blind evaluation:
- CPM-generated answers were preferred in 19 out of 26 cases
- Accuracy improvement: ~73% vs monolithic prompting
Observed reasons for preference:
Monolithic Prompt Issues
- Important information was often buried inside the 20k-token block.
- Responses were more generic and less specific.
- Conflicting rules from unrelated modules created inconsistencies.
- Reviewers reported “lost in the middle” effects consistent with academic research.
CPM Advantages
- Smaller and more relevant context leads to sharper, more grounded answers.
- Domain-specific rules are only loaded when necessary.
- Reduced noise improves the model’s reasoning and recall of key details.
- Responses followed internal standards more reliably.
5. Why Modular Context Improves Accuracy
Large prompts do not simply “give the AI more information”. They introduce several well-known failure modes:
5.1 Information Dilution
When everything is included, the model distributes attention across irrelevant or conflicting data.
5.2 “Lost in the Middle” Effect
Research shows that long contexts reduce recall for information placed in the middle of the prompt. With ~20k tokens, most modules fall into this zone.
5.3 Instruction Interference
Different parts of a long system prompt can contain rules that overlap or contradict each other. Models respond inconsistently when multiple high-level instructions coexist.
5.4 Higher Chance of Generalization
Because the model is overloaded, it tends to produce vague or high-level responses rather than precise, actionable ones.
By activating only the relevant modules, CPM removes these issues entirely.
6. Impact on the Client’s Workflow
After integrating CPM:
- The internal AI assistant became more predictable and aligned with the firm’s standards.
- Developers could adjust modules without touching application code.
- Costs dropped significantly for the same workload.
- Response rejection rate decreased (fewer “retry” messages).
- Reviewers reported higher trust in the system’s answers.
The client has continued to increase usage over time.
7. Improvements Made as a Result of This Study
Based on real feedback and the findings above, we implemented several upgrades to the CPM:
- Improved module activation logic
- Better token preview and context inspection
- New UI components for context grouping
- Optimized merging strategy for system instructions
- Extended analytics in BrinPage Platform for monitoring token usage
These improvements shipped in late November 2025.
8. Conclusion
Modular prompting with BrinPage CPM led to substantial improvements in both cost and accuracy when compared with a traditional monolithic prompt.
- ~6–7× less context per request
- ~70% lower API costs
- ~73% accuracy preference in blind evaluation
- More stable, consistent and domain-aligned responses
- Better maintainability for teams managing large context bases
This real-world case demonstrates that as context size grows, modularization becomes not only beneficial but essential for high-quality AI systems.
9. Availability
The full study (including methodology, charts, and prompt structures) will be maintained and updated at:
docs.brinpage.com/case-studies/modular-context-analysis
All client-identifying information has been removed to preserve privacy.